In analyzing genetic data, how do we know whether deviation from the expected ratio is due to chance rather than to another, independent factor?

In a cross between a black and a white guinea pig, all members of the F₁ generation are black. The F₂ generation is made up of approximately 3/4 black and 1/4 white guinea pigs. Diagram this cross, showing the genotypes and phenotypes.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Mendelian Inheritance and Dominance
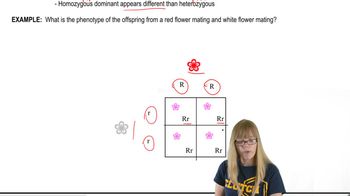
Punnett Square and Genotypic Ratios

Homozygous and Heterozygous Genotypes

Since experimental crosses are not performed in humans, how do we know how traits are inherited?
Write a short essay that correlates Mendel's four postulates with what is now known about genes, alleles, and homologous chromosomes.
Albinism in humans is inherited as a simple recessive trait. For the following families, determine the genotypes of the parents and offspring. (When two alternative genotypes are possible, list both.)
Two normal parents have five children, four normal and one albino.
Albinism in humans is inherited as a simple recessive trait. For the following families, determine the genotypes of the parents and offspring. (When two alternative genotypes are possible, list both.)
A normal male and an albino female have six children, all normal.
Which of Mendel's postulates are illustrated by the pedigree that you constructed in Problem 3? List and define these postulates.
