Textbook Question
Write the electron configuration for oxygen. Then write the Lewis symbol for oxygen and show which electrons from the electron configuration are included in the Lewis symbol.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

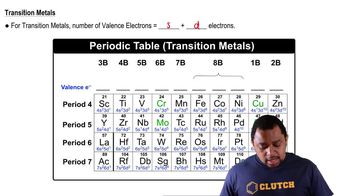
Write the electron configuration for oxygen. Then write the Lewis symbol for oxygen and show which electrons from the electron configuration are included in the Lewis symbol.
Write the Lewis symbol for each atom or ion. b. K+
Write the Lewis symbol for each atom or ion. d. S2-
Write the Lewis symbols for the ions in each ionic compound. d. K2O
Write the Lewis symbols for the ions in each ionic compound. a. SrO d. RbF