Textbook Question
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. b. CH3OCH3

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

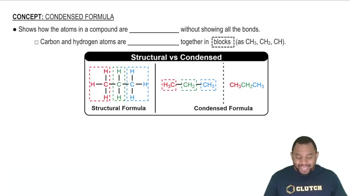
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. b. CH3OCH3
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. c. CH3COCH3
Use Lewis structures to explain why Br3- and I3- are stable, while F3- is not.