The elements with atomic numbers 35 and 53 have similar chemical properties. Based on their electronic configurations, predict the atomic number of a heavier element that also should share these chemical properties.
Ch.9 - Periodic Properties of the Elements

Chapter 9, Problem 109
You have cracked a secret code that uses elemental symbols to spell words. The code uses numbers to designate the elemental symbols. Each number is the sum of the atomic number and the highest principal quantum number of the highest occupied orbital of the element whose symbol is to be used. The message may be written forward or backward. Decode the following messages: a. 10, 12, 58, 11, 7, 44, 63, 66
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the code. The code uses numbers that are the sum of the atomic number (Z) and the highest principal quantum number (n) of the highest occupied orbital of the element. The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom, and the principal quantum number is the main energy level of an electron. The sum of these two numbers gives you the code number for each element.
Step 2: For each number in the message, you need to find an element whose atomic number and highest principal quantum number add up to that number. This can be done by referring to a periodic table. Remember that the principal quantum number corresponds to the period (row) in which the element is located.
Step 3: Once you have identified the elements, write down their symbols in the order they appear in the message. If the message doesn't make sense, try reading it backward, as the message may be written in reverse.
Step 4: If you're having trouble finding an element that fits a particular number, remember that the highest principal quantum number is the period number. So, for larger numbers, you'll be looking for elements in the lower periods with larger atomic numbers.
Step 5: Keep in mind that some numbers may correspond to more than one element. If the message doesn't make sense with one element, try using the other.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Atomic Number
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom of that element. It uniquely identifies an element and determines its position in the periodic table. For example, carbon has an atomic number of 6, meaning it has 6 protons.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Atom Structure
Principal Quantum Number
The principal quantum number (n) indicates the main energy level occupied by an electron in an atom. It is a positive integer (n=1, 2, 3, ...) and helps determine the size and energy of the orbital. The highest principal quantum number of the highest occupied orbital reflects the outermost electron shell of an atom.
Recommended video:
Guided course
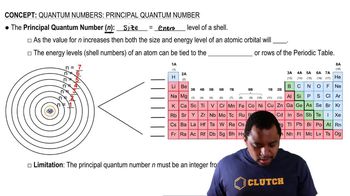
Principal Quantum Number
Elemental Symbols
Elemental symbols are one- or two-letter abbreviations used to represent chemical elements in the periodic table. For instance, 'H' stands for hydrogen and 'O' for oxygen. In the context of the secret code, these symbols are used to decode messages based on the numerical values derived from atomic numbers and quantum numbers.
Recommended video:
Guided course
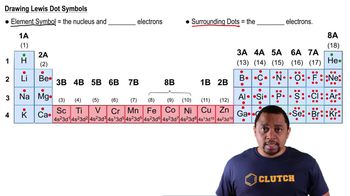
Lewis Dot Symbols
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Use Coulomb's law to calculate the ionization energy in kJ/mol of an atom composed of a proton and an electron separated by 110.00 pm. What wavelength of light has sufficient energy to ionize the atom?
Textbook Question
The first ionization energy of lithium is 520 kJ/mol. Use Coulomb's law to estimate the average distance between the lithium nucleus and the 2s electron. How does this distance compare to the atomic radius of lithium? Assume an effective nuclear charge of 1+ for the valence electron.
Textbook Question
Consider the elements: B, C, N, O, F. d. Which element has three unpaired electrons?
