Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Kinetic Molecular Theory
The Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) explains the behavior of gases in terms of particles in constant motion. It posits that gas particles are in continuous, random motion and that their collisions with each other and the walls of their container are perfectly elastic. This theory helps to describe properties such as pressure, temperature, and volume in gases.
Recommended video:
Ideal Gas Behavior
Ideal gas behavior refers to the assumptions made in the Kinetic Molecular Theory that gases behave ideally under certain conditions, specifically at high temperatures and low pressures. Under these conditions, the volume of gas particles is negligible, and intermolecular forces are minimal. However, deviations from ideal behavior occur at low temperatures and high pressures, where interactions between particles become significant.
Recommended video:
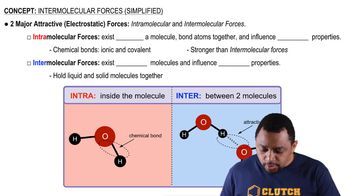
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules that influence their physical properties. At low temperatures, these forces become more pronounced as the kinetic energy of the particles decreases, leading to potential condensation or solidification. This breakdown of the assumption of negligible intermolecular forces is a key limitation of the Kinetic Molecular Theory under low-temperature conditions.
Recommended video:
Intermolecular vs Intramolecular Forces
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance