Write the balanced chemical equation for each reaction. b. Solid iron(III) oxide reacts with hydrogen gas to form solid iron and liquid water.
Ch.4 - Chemical Reactions and Chemical Quantities

Chapter 4, Problem 24
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of aqueous potassium hydroxide with aqueous iron(III) chloride to form solid iron(III) hydroxide and aqueous potassium chloride.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the reactants and their states: potassium hydroxide (KOH) is aqueous, and iron(III) chloride (FeCl3) is also aqueous.
Identify the products and their states: iron(III) hydroxide (Fe(OH)3) is a solid, and potassium chloride (KCl) is aqueous.
Write the unbalanced chemical equation with the correct states: \(\text{KOH}_{(aq)} + \text{FeCl}_3_{(aq)} \rightarrow \text{Fe(OH)}_3_{(s)} + \text{KCl}_{(aq)}\).
Balance the chemical equation by adjusting the coefficients to ensure the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation. Start by balancing the iron and potassium atoms, then the chlorine and oxygen atoms.
Check the final balanced equation to ensure mass and charge are balanced.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations involves ensuring that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides. This is based on the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. To balance an equation, coefficients are adjusted in front of the chemical formulas.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Chemical Equations
Types of Chemical Reactions
The reaction described is a double displacement reaction, where two compounds exchange ions to form new compounds. In this case, potassium hydroxide and iron(III) chloride react to form iron(III) hydroxide and potassium chloride. Recognizing the type of reaction helps in predicting the products and understanding the underlying chemistry.
Recommended video:
Guided course
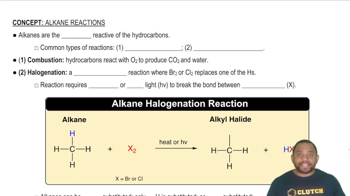
Common Types of Alkane Reactions
Solubility Rules
Solubility rules are guidelines that help predict whether a compound will dissolve in water. For instance, potassium chloride is soluble in water, while iron(III) hydroxide is not, leading to its precipitation as a solid. Understanding solubility is crucial for determining the physical states of reactants and products in a chemical equation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
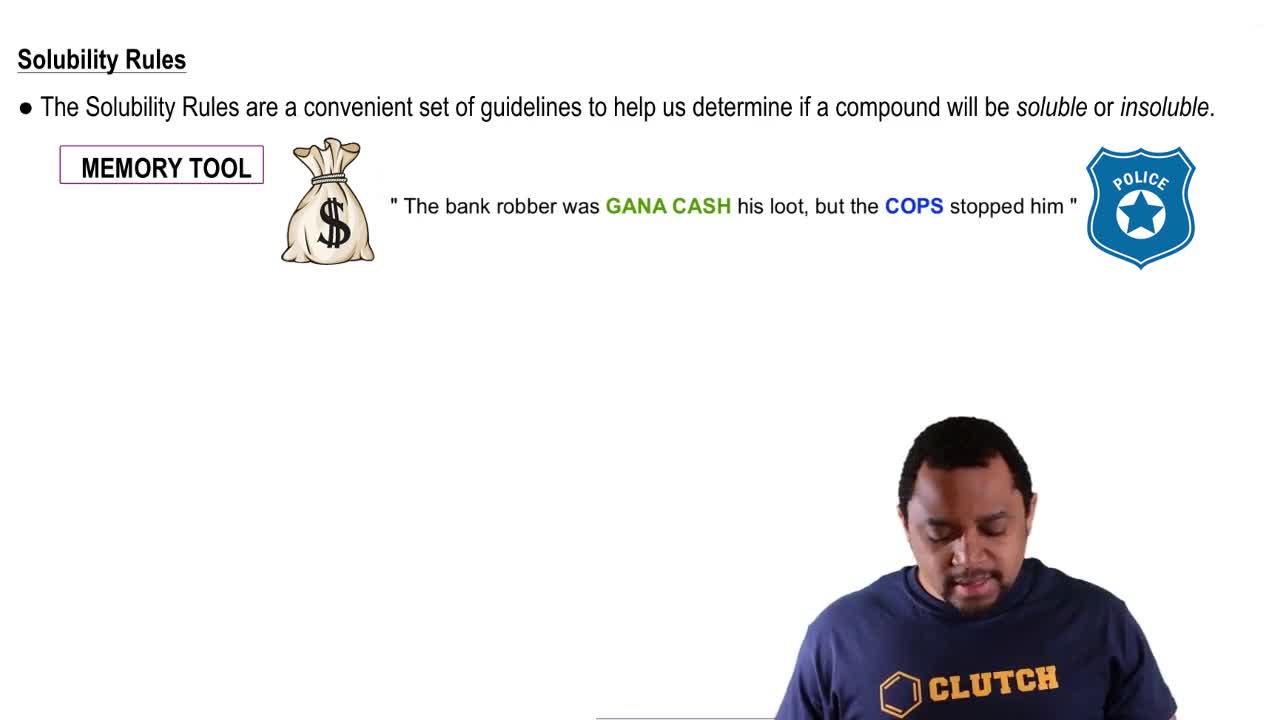
Solubility Rules
Related Practice
Textbook Question
4
views
Textbook Question
Write the balanced chemical equation for each reaction.
c. Sulfur dioxide gas reacts with oxygen gas to form sulfur trioxide gas.
d. Gaseous ammonia (NH3) reacts with gaseous oxygen to form gaseous nitrogen monoxide and gaseous water.
1
views
Textbook Question
Balance each chemical equation. b. Co(NO3)3(aq) + (NH4)2S(aq) → Co2S3(s) + NH4NO3(aq)
1
views
Textbook Question
Consider the unbalanced equation for the neutralization of acetic acid: HC2H3O2(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) → H2O(l) + Ba(C2H3O2)2(aq) Balance the equation and determine how many moles of Ba(OH)2 are required to completely neutralize 1.22 mol of HC2H3O2.
Textbook Question
Balance the equation and calculate how many moles of O2 form when each quantity of reactant completely reacts. N2O5( g) → NO2(g) + O2(g) a. 1.2 mol N2O5
