Textbook Question
Write the formula for each ionic compound. f. potassium hydrogen carbonate

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

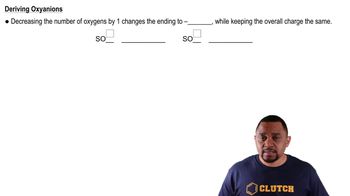

Write the formula for each ionic compound. f. potassium hydrogen carbonate
Name each ionic compound containing a polyatomic ion. a. Ba(OH)2 b. NH4I c. NaBrO4 d. Fe(OH)3
Name each ionic compound. a. Mg3N2 b. KF c. Na2O d. Li2S f. KI e. CsF
Name each ionic compound. a. SnCl4 b. PbI2 c. Fe2O3 d. CuI2 e. HgBr2 f. CrCl2
Write the formula for each ionic compound. a. sodium hydrogen sulfite b. lithium permanganate c. silver nitrate d. potassium sulfate e. rubidium hydrogen sulfate