Textbook Question
Predict a likely mode of decay for each unstable nuclide. a. Ca-35

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
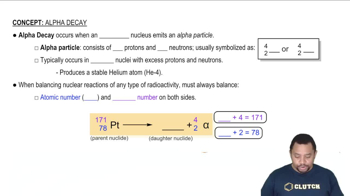

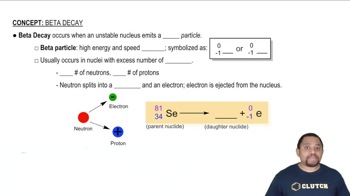
Predict a likely mode of decay for each unstable nuclide. a. Ca-35
Predict a likely mode of decay for each unstable nuclide. b. Al-34
Predict a likely mode of decay for each unstable nuclide. a. C-16
Which nuclide in each pair would you expect to have the longer half-life? a. Cs-149 or Cs-139 b. Fe-45 or Fe-52
One of the nuclides in spent nuclear fuel is U-235, an alpha emitter with a half-life of 703 million years. How long will it take for the amount of U-235 to reach 10.0% of its initial amount?