Textbook Question
Write the nuclear equation for the fusion of two H-2 atoms to form He-3 and one neutron.
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance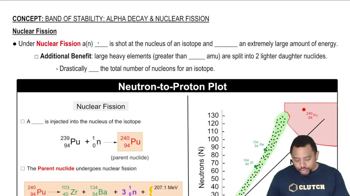

Write the nuclear equation for the fusion of two H-2 atoms to form He-3 and one neutron.
Write the nuclear reaction for the neutron-induced fission of U-235 to produce Te-137 and Zr-97. How many neutrons are produced in the reaction?
Write the nuclear equation for the fusion of H-3 with H-1 to form He-4.
Rutherfordium-257 was synthesized by bombarding Cf-249 with C-12. Write the nuclear equation for this reaction.