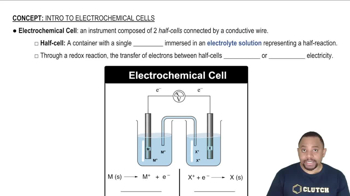
Standard Cell Potential
The standard cell potential, denoted as E°, is the measure of the voltage produced by an electrochemical cell under standard conditions (1 M concentration, 1 atm pressure, and 25°C). It indicates the tendency of a chemical reaction to occur spontaneously; a positive E° value suggests a spontaneous reaction, while a negative value indicates non-spontaneity.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance