Textbook Question
Use tabulated electrode potentials to calculate 𝛥𝐺rxn° for each reaction at 25 °C. c. Br2(l) + 2Cl–(aq) → 2 Br–(aq) + Cl2(g)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

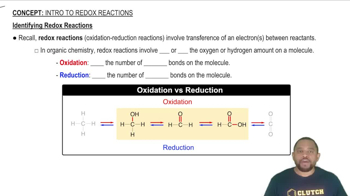

Use tabulated electrode potentials to calculate 𝛥𝐺rxn° for each reaction at 25 °C. c. Br2(l) + 2Cl–(aq) → 2 Br–(aq) + Cl2(g)
Calculate the equilibrium constant for each of the reactions in Problem 70.
A voltaic cell employs the following redox reaction: Sn2+(aq) + Mn(s) → Sn(s) + Mn2+(aq) Calculate the cell potential at 25 °C under each set of conditions. c. [Sn2+] = 2.00 M; [Mn2+] = 0.0100 M