For each pair of substances, choose the one that you expect to have the higher standard molar entropy (S°) at 25 °C. Explain your choices. a. CO(g); CO2(g) b. CH3OH(l); CH3OH(g) c. Ar(g); CO2(g) d. CH4(g); SiH4(g) e. NO2(g); CH3CH2CH3(g) f. NaBr(s); NaBr(aq)
Ch.19 - Free Energy & Thermodynamics

Chapter 19, Problem 56
Rank each set of substances in order of increasing standard molar entropy (S°). Explain your reasoning. a. I2(g); F2(g); Br2(g); Cl2(g) b. H2O(g); H2O2(g); H2S(g) c. C(s, graphite); C(s, diamond); C(s, amorphous)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the substances involved: graphite, diamond, and amorphous carbon, all of which are allotropes of carbon.
Recall that standard molar entropy (S°) is a measure of the disorder or randomness of a system. Generally, more ordered structures have lower entropy.
Consider the structure of each allotrope: Graphite has a layered structure with more freedom of movement between layers, diamond has a rigid 3D lattice, and amorphous carbon lacks a long-range order.
Compare the order of the structures: Diamond, with its highly ordered lattice, is expected to have the lowest entropy. Graphite, with its layered structure, is more disordered than diamond. Amorphous carbon, being the least ordered, should have the highest entropy.
Rank the substances in order of increasing standard molar entropy: C(s, diamond) < C(s, graphite) < C(s, amorphous).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Standard Molar Entropy
Standard molar entropy (S°) is a measure of the randomness or disorder of a substance at standard conditions (1 bar, 25°C). It reflects the number of accessible microstates for a given amount of substance, with higher values indicating greater disorder. Entropy increases with temperature, molecular complexity, and the number of particles in a system.
Recommended video:
Guided course
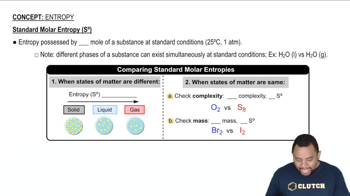
Standard Molar Entropy
Allotropes of Carbon
Carbon exists in several allotropes, including graphite, diamond, and amorphous carbon. Each allotrope has a distinct arrangement of carbon atoms, affecting its physical properties and entropy. Graphite has a layered structure allowing for more disorder, while diamond has a rigid, ordered structure, and amorphous carbon lacks a defined structure, contributing to its higher entropy.
Recommended video:
Guided course
3 and 4 Carbon Alkyls
Factors Affecting Entropy
Several factors influence the standard molar entropy of substances, including molecular structure, phase (solid, liquid, gas), and temperature. Generally, gases have higher entropies than liquids, and liquids have higher entropies than solids. Among solids, those with more complex structures or greater molecular motion tend to have higher entropies, which is crucial for ranking the given carbon allotropes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Factors Affecting Entropy
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Rank each set of substances in order of increasing standard molar entropy (S°). Explain your reasoning. a. NH3(g); Ne(g); SO2(g); CH3CH2OH(g); He(g) c. CH4(g); CF4(g); CCl4(g)
1
views
Textbook Question
Rank each set of substances in order of increasing standard molar entropy (S°). Explain your reasoning. b. H2O(s); H2O(l); H2O(g)
1
views
Textbook Question
Use data from Appendix IIB to calculate ΔS°rxn for each of the reactions. In each case, try to rationalize the sign of ΔS°rxn . b. C(s) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + H2(g)
Textbook Question
Use data from Appendix IIB to calculate ΔS°rxn for each of the reactions. In each case, try to rationalize the sign of ΔS°rxn. c. CO(g) + H2O(g) → H2(g) + CO2(g)
