The reaction A¡products was monitored as a function of time. The results are shown here. Time (s) [A] (M) 0 1.000 25 0.914 50 0.829 75 0.744 100 0.659 125 0.573 150 0.488 175 0.403 200 0.318 Determine the order of the reaction and the value of the rate constant. What is the rate of reaction when [A] = 0.10 M?

a. What is the half-life for the first-order decomposition of SO2Cl2 with a rate constant of 1.42 x 10^-4 s^-1? b. How long will it take for the concentration of SO2Cl2 to decrease to 25% of its initial concentration? c. If the initial concentration of SO2Cl2 is 1.00 M, how long will it take for the concentration to decrease to 0.78 M? d. If the initial concentration of SO2Cl2 is 0.150 M, what is the concentration of SO2Cl2 after 2.00 x 10^2 s? After 5.00 x 10^2 s?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
First-Order Reactions
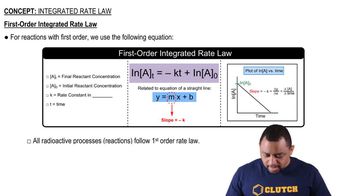
Half-Life

Exponential Decay
This reaction was monitored as a function of time: A → B + C A plot of ln[A] versus time yields a straight line with slope -0.0105/s. a. What is the value of the rate constant (k) for this reaction at this temperature?
This reaction was monitored as a function of time: AB → A + B A plot of 1/[AB] versus time yields a straight line with a slope of +0.25/Ms. b. Write the rate law for the reaction.
Silver nitrate solutions are often used to plate silver onto other metals. What is the maximum amount of silver (in grams) that can be plated out of 4.8 L of an AgNO3 solution containing 3.4% Ag by mass? Assume that the density of the solution is 1.01 g/mL.
The decomposition of XY is second order in XY and has a rate constant of 7.02⨉10-3 M-1• s-1 at a certain temperature. a. What is the half-life for this reaction at an initial concentration of 0.100 M?
