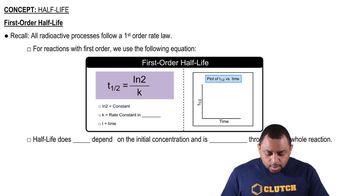
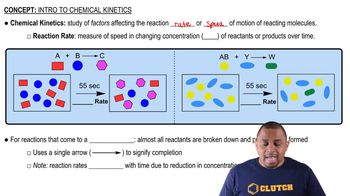
Consider the tabulated data showing the initial rate of a reaction (A → products) at several different concentrations of A. What is the order of the reaction? Write a rate law for the reaction including the value of the rate constant, k.
[A] (M) Initial Rate (M/s)
0.050 0.100
0.075 0.225
0.090 0.324