Textbook Question
Identify each solid as molecular, ionic, or atomic. a. Ru(s)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
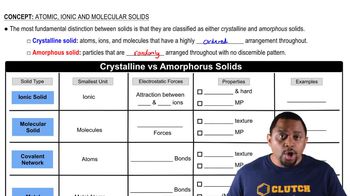


Identify each solid as molecular, ionic, or atomic. a. Ru(s)
Plonium crystallizes with a simple cubic structure. It has a density of 9.3 g/cm3, a radius of 167 pm, and a molar mass of 209 g/mol. Use these data to calculate Avogadro's number (the number of atoms in one mole).
Identify each solid as molecular, ionic, or atomic. d. Xe(s)
Which solid has the highest melting point? Why? C(s, diamond), Kr(s), NaCl(s), H2O(s)
Which solid in each pair has the higher melting point and why?
a. TiO2(s) or HOOH(s)
b. CCl4(s) or SiCl4(s)
c. Kr(s) or Xe(s)