Textbook Question
Which compound would you expect to have greater surface tension: acetone [(CH3)2CO] or water (H2O)? Explain.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
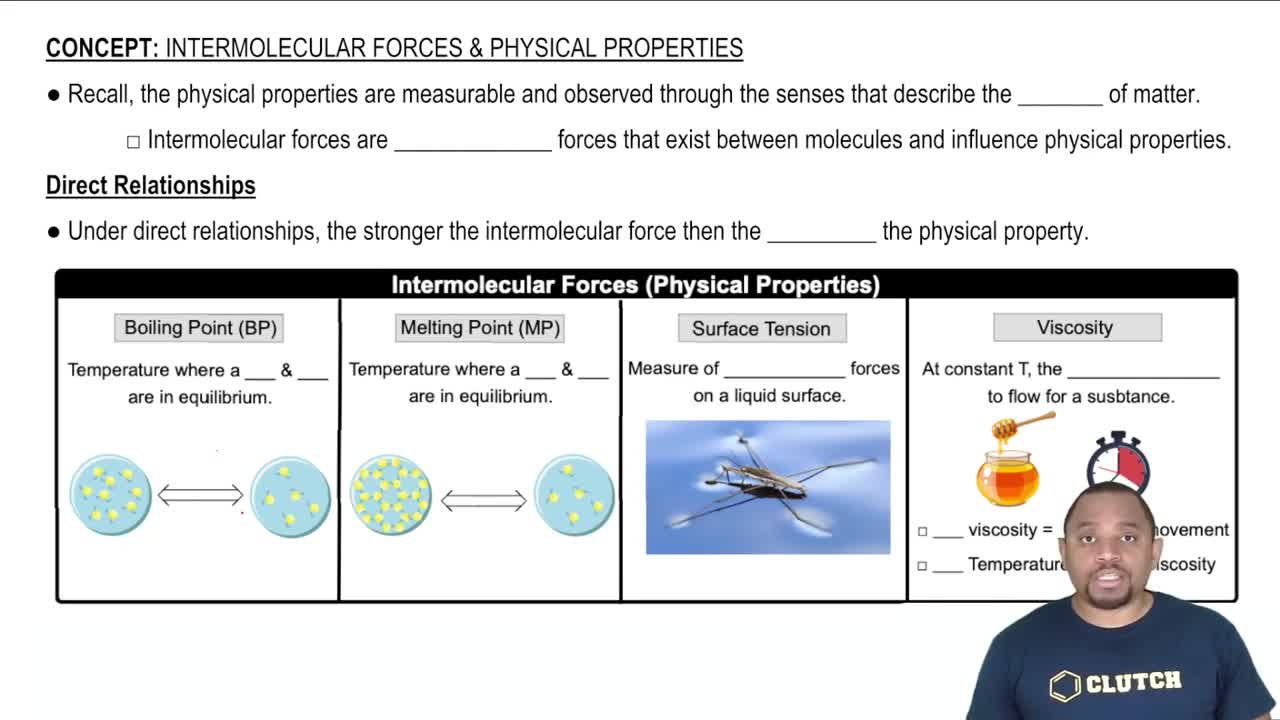

Which compound would you expect to have greater surface tension: acetone [(CH3)2CO] or water (H2O)? Explain.
Explain why the viscosity of multigrade motor oils is less temperature-dependent than that of single-grade motor oils.
When a thin glass tube is put into water, the water rises 1.4 cm. When the same tube is put into hexane, the hexane rises only 0.4 cm. Explain.
Which evaporates more quickly: 100 mL of water (H2O) in a beaker or 100 mL of acetone [(CH3)2CO] in an identical beaker under identical conditions? Is the vapor pressure of the two substances different? Explain.