Textbook Question
Determine the kinds of intermolecular forces that are present in each element or compound. a. HBr

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance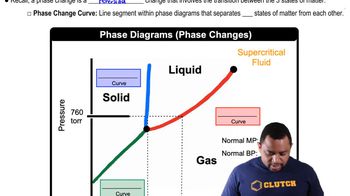

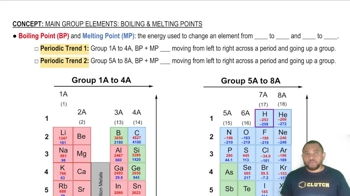
Determine the kinds of intermolecular forces that are present in each element or compound. a. HBr
Determine the kinds of intermolecular forces that are present in each element or compound. b. I2
Determine the kinds of intermolecular forces that are present in each element or compound. d. CH3OH