Textbook Question
Determine the kinds of intermolecular forces that are present in each element or compound. d. CH3OH

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance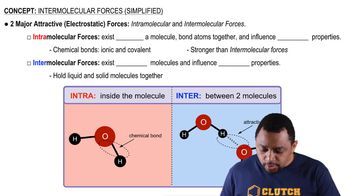

Determine the kinds of intermolecular forces that are present in each element or compound. d. CH3OH
Determine the kinds of intermolecular forces that are present in each element or compound. c. CCl4
Determine the kinds of intermolecular forces that are present in each element or compound. d. N2
In each pair of compounds, pick the one with the higher boiling point. Explain your reasoning. c. CH3OCH3 or CH3CH3OH
In each pair of compounds, pick the one with the higher boiling point. Explain your reasoning. b. CH3OH or CH3SH