Textbook Question
Determine if a bond between each pair of atoms would be pure covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. a. Br and Br

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
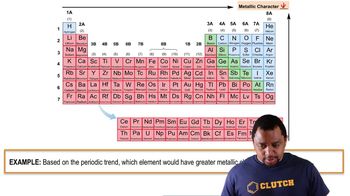


Determine if a bond between each pair of atoms would be pure covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. a. Br and Br
Refer to Figure 10.10 to estimate the percent ionic character of the CO bond.
Draw the Lewis structure for BrF with an arrow representing the dipole moment. Refer to Figure 10.10 to estimate the percent ionic character of the BrF bond.
Write the Lewis structure for each molecule or ion. b. OH-
Write the Lewis structure for each molecule or ion. c. BrO-
Write the Lewis structure for each molecule or ion. d. C2H4