Order these compounds in order of decreasing carbon–carbon bond length: HCCH, H2CCH2, H3CCH3.

Ethanol is a possible fuel. Use average bond energies to calculate ΔHrxn for the combustion of ethanol. CH3CH2OH(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 3 H2O(g)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Bond Energies
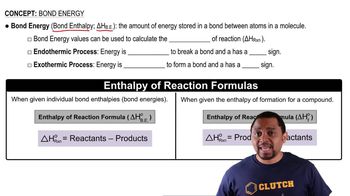
Enthalpy Change (ΔHrxn)

Combustion Reaction
Which of the two compounds, H2NNH2 and HNNH, has the strongest nitrogen-nitrogen bond, and which has the shorter nitrogen-nitrogen bond.
Hydrogenation reactions are used to add hydrogen across double bonds in hydrocarbons and other organic compounds. Use average bond energies to calculate ΔHrxn for the hydrogenation reaction. H2C=CH2(g) + H2(g) → H3C–CH3(g)
Ethane burns in air to form carbon dixode and water vapor.
2 H3C¬CH3( g) + 7 O2( g)¡4 CO2( g) + 6 H2O( g)
Use average bond energies to calculate ΔHrxn for the reaction.
In the Chemistry and the Environment box on free radicals in this chapter, we discussed the importance of the hydroxyl radical in reacting with and eliminating many atmospheric pollutants. However, the hydroxyl radical does not clean up everything. For example, chlorofluorocarbons—which destroy stratospheric ozone—are not attacked by the hydroxyl radical. Consider the hypothetical reaction by which the hydroxyl radical might react with a chlorofluorocarbon: OH(g) + CF2Cl2(g) → HOF(g) + CFCl2(g) Use bond energies to explain why this reaction is improbable. (The C–F bond energy is 552 kJ/mol.)
