Textbook Question
Write the full orbital diagram for each element. a. N b. F c. Mg d. Al

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

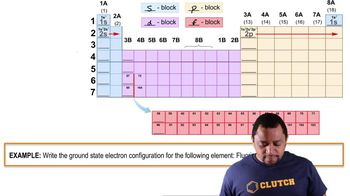
Write the full orbital diagram for each element. a. N b. F c. Mg d. Al
Write the full orbital diagram for each element. a. S
Write the full orbital diagram for each element. b. Ca
Use the periodic table to write an electron configuration for each element. Represent core electrons with the symbol of the previous noble gas in brackets. c. Zr
Use the periodic table to determine the element corresponding to each electron configuration. a. [Ar] 4s23d104p6 b. [Ar] 4s23d2 c. [Kr] 5s24d105p2
Use the periodic table to write an electron configuration for each element. Represent core electrons with the symbol of the previous noble gas in brackets. a. P b. Ge c. I