Textbook Question
Which is the larger species in each pair? a. Li or Li+ b. Cs- or Cs+ c. Cr- or Cr3+ d. O or O2-
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance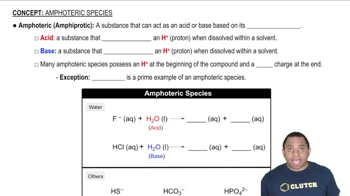


Which is the larger species in each pair? a. Li or Li+ b. Cs- or Cs+ c. Cr- or Cr3+ d. O or O2-
Write orbital diagrams for each ion and determine if the ion is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. a. Cd2+ b. Au+ c. Mo3+ d. Zr2+
Which is the larger species in each pair? a. Sr or Sr2+ b. N or N3- c. Ni or Ni2+ d. S2- or Ca2+
Arrange this isoelectronic series in order of increasing atomic radius: Se2- , Sr2+ , Rb+ , Br- .
Choose the element with the higher first ionization energy from each pair. a. Br or Bi
Choose the element with the higher first ionization energy from each pair. b. Na or Rb