Charcoal is primarily carbon. Determine the mass of CO2 produced by burning enough carbon (in the form of charcoal) to produce 5.00×102 kJ of heat. C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ΔH°rxn = –393.5 kJ

A 31.1-g wafer of pure gold, initially at 69.3 °C, is submerged into 64.2 g of water at 27.8 °C in an insulated container. What is the final temperature of both substances at thermal equilibrium?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Thermal Equilibrium

Specific Heat Capacity
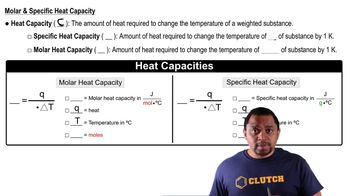
Heat Transfer Equation

A silver block, initially at 58.5 °C, is submerged into 100.0 g of water at 24.8 °C, in an insulated container. The final temperature of the mixture upon reaching thermal equilibrium is 26.2 °C. What is the mass of the silver block?
A 32.5-g iron rod, initially at 22.7 °C, is submerged into an unknown mass of water at 63.2 °C, in an insulated container. The final temperature of the mixture upon reaching thermal equilibrium is 59.5 °C. What is the mass of the water?
A 2.85-g lead weight, initially at 10.3 °C, is submerged in 7.55 g of water at 52.3 °C in an insulated container. What is the final temperature of both substances at thermal equilibrium?
Two substances, A and B, initially at different temperatures, come into contact and reach thermal equilibrium. The mass of substance A is 6.15 g and its initial temperature is 20.5 °C. The mass of substance B is 25.2 g and its initial temperature is 52.7 °C. The final temperature of both substances at thermal equilibrium is 46.7 °C. If the specific heat capacity of substance B is 1.17 J/g•°C, what is the specific heat capacity of substance A?
Exactly 1.5 g of a fuel burns under conditions of constant pressure and then again under conditions of constant volume. In measurement A the reaction produces 25.9 kJ of heat, and in measurement B the reaction produces 23.3 kJ of heat. Which measurement (A or B) corresponds to conditions of constant pressure? Explain.
