A gaseous hydrogen- and carbon-containing compound is decomposed and found to contain 82.66% carbon and 17.34% hydrogen by mass. The mass of 158 mL of the gas, measured at 556 mmHg and 25 °C, was 0.275 g. What is the molecular formula of the compound?
Ch.6 - Gases

Chapter 6, Problem 101
Consider the reaction: 2 NiO(s) → 2 Ni(s) + O2(g). If O2 is collected over water at 40.0 °C and a total pressure of 745 mmHg, what volume of gas is collected for the complete reaction of 24.78 g of NiO?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Calculate the molar mass of NiO by adding the atomic masses of Ni and O.
Determine the number of moles of NiO by dividing the given mass (24.78 g) by the molar mass of NiO.
Use the stoichiometry of the balanced chemical equation to find the moles of O2 produced. According to the equation, 2 moles of NiO produce 1 mole of O2.
Use the ideal gas law, PV = nRT, to calculate the volume of O2. First, convert the temperature from Celsius to Kelvin by adding 273.15.
Adjust the total pressure to account for the vapor pressure of water at 40.0 °C, then use the adjusted pressure in the ideal gas law to find the volume of O2.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions based on the balanced equation. It allows us to determine the amount of product formed or reactant consumed from a given quantity of another substance. In this case, we need to use the molar ratios from the balanced equation to find out how much O2 is produced from the decomposition of NiO.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Stoichiometry Concept
Gas Laws
Gas laws describe the behavior of gases in relation to pressure, volume, and temperature. The Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT) is particularly useful for calculating the volume of gas produced under specific conditions. In this scenario, we will apply the gas laws to determine the volume of O2 collected, taking into account the total pressure and the vapor pressure of water at 40.0 °C.
Recommended video:
Guided course
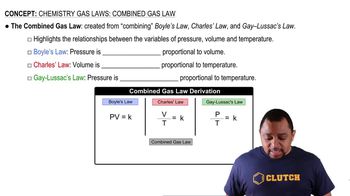
Combined Gas Law
Vapor Pressure of Water
The vapor pressure of water is the pressure exerted by water vapor in equilibrium with its liquid at a given temperature. At 40.0 °C, the vapor pressure of water must be subtracted from the total pressure to find the partial pressure of the O2 gas collected. This adjustment is crucial for accurately calculating the volume of O2 produced in the reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course
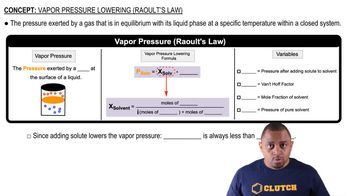
Raoult's Law and Vapor Pressure
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
A gaseous hydrogen- and carbon-containing compound is decomposed and found to contain 85.63% C and 14.37% H by mass. The mass of 258 mL of the gas, measured at STP, was 0.646 g. What is the molecular formula of the compound?
Textbook Question
Consider the reaction: 2 Ag2O(s) → 4 Ag(s) + O2(g) If this reaction produces 15.8 g of Ag(s), what total volume of gas can be collected over water at a temperature of 25 °C and a total pressure of 752 mmHg?
Textbook Question
Consider the reaction:
2 SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2 SO3(g)
a. If 285.5 mL of SO2 reacts with 158.9 mL of O2 (both measured at 315 K and 50.0 mmHg), what is the limiting reactant and the theoretical yield of SO3?
