Combustion analysis of naphthalene, a hydrocarbon used in mothballs, produces 8.80 g CO2 and 1.44 g H2O. Calculate the empirical formula of naphthalene.
Ch.3 - Molecules and Compounds

Chapter 3, Problem 101
Classify each compound as organic or inorganic: a. CaCO3 b. C4H8 c. C4H6O6 d. LiF
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the definition of organic and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds primarily contain carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms, often with other elements like oxygen, nitrogen, etc. Inorganic compounds typically do not have carbon-hydrogen bonds.
Examine compound a: \( \text{CaCO}_3 \). This compound contains calcium, carbon, and oxygen. It is a salt and does not have carbon-hydrogen bonds, classifying it as inorganic.
Examine compound b: \( \text{C}_4\text{H}_8 \). This compound consists solely of carbon and hydrogen, which are typical of organic compounds. Therefore, it is classified as organic.
Examine compound c: \( \text{C}_4\text{H}_6\text{O}_6 \). This compound contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The presence of carbon and hydrogen together suggests it is an organic compound.
Examine compound d: \( \text{LiF} \). This compound consists of lithium and fluorine, with no carbon present. It is classified as inorganic.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are primarily composed of carbon atoms, often in combination with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements. They typically contain carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds and are associated with living organisms. Examples include hydrocarbons and functional groups like alcohols and acids.
Recommended video:
Guided course
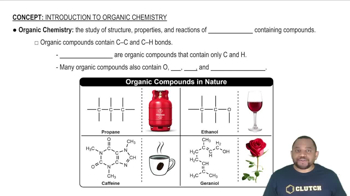
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Inorganic Compounds
Inorganic compounds generally do not contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and include a wide range of substances such as minerals, metals, and salts. They can be composed of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, and often have ionic or covalent bonds. Examples include sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ionic Compounds Naming
Classification Criteria
The classification of compounds as organic or inorganic is based on their molecular structure and composition. Organic compounds must contain carbon and typically hydrogen, while inorganic compounds may contain carbon but lack C-H bonds. This distinction is crucial for understanding chemical behavior and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Guided course
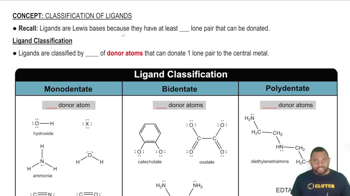
Ligand Classification
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The foul odor of rancid butter is due largely to butyric acid, a compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Combustion analysis of a 4.30-g sample of butyric acid produces 8.59 g CO2 and 3.52 g H2O. Determine the empirical formula of butyric acid.
Textbook Question
Tartaric acid is the white, powdery substance that coats tart candies such as Sour Patch Kids. Combustion analysis of a 12.01-g sample of tartaric acid—which contains only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen—produces 14.08 g CO2 and 4.32 g H2O. Determine the empirical formula of tartaric acid.
1
views
Textbook Question
Classify each hydrocarbon as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. a. H2C=CH−CH3 b. H3C−CH2−CH3 c. HC≡C−CH3 d. H3C−CH2−CH2−CH3
Textbook Question
Classify each hydrocarbon as an alkane, alkene, or alkyne. a. HC≡CH
1
views
