A 75-kg human has a dose of 32.8 rad of radiation. How much energy is absorbed by the person's body? Compare this energy to the amount of energy absorbed by the person's body if he or she jumped from a chair to the floor (assume that the chair is 0.50 m from the ground and that all of the energy from the fall is absorbed by the person).
Ch.21 - Radioactivity & Nuclear Chemistry

Chapter 21, Problem 74
If a 55-gram laboratory mouse is exposed to a dose of 20.5 rad of radiation, how much energy is absorbed by the mouse’s body?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that 1 rad is equivalent to 0.01 joules of energy absorbed per kilogram of tissue.
Calculate the mass of the mouse in kilograms by converting grams to kilograms. (55 grams = 0.055 kilograms)
Use the formula: Energy absorbed (in joules) = dose (in rads) × mass (in kg) × 0.01 J/kg per rad.
Substitute the given values into the formula: Energy absorbed = 20.5 rads × 0.055 kg × 0.01 J/kg per rad.
Perform the multiplication to find the energy absorbed in joules.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Radiation Dose
Radiation dose, measured in units such as rad, quantifies the amount of energy absorbed by a material, typically biological tissue, from ionizing radiation. One rad is defined as the absorption of 100 ergs of energy per gram of tissue. Understanding this concept is crucial for calculating the energy absorbed by the mouse based on its mass and the radiation dose it receives.
Recommended video:
Guided course
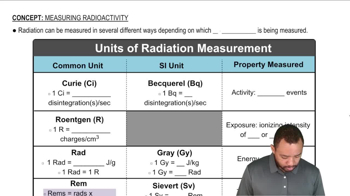
Units of Radiation Measurement
Energy Absorption Calculation
To determine the energy absorbed by an object from radiation, the formula used is: Energy (in ergs) = Dose (in rads) × Mass (in grams). This relationship allows for the straightforward calculation of energy absorbed by multiplying the radiation dose by the mass of the object, which in this case is the laboratory mouse.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Gibbs Free Energy of Reactions
Unit Conversion
In scientific calculations, it is often necessary to convert units to ensure consistency and accuracy. For example, while energy may be expressed in ergs, it can also be converted to joules (1 erg = 10^-7 joules). Understanding unit conversion is essential for interpreting results and ensuring that calculations align with standard scientific practices.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Conversion Factors
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
Suppose a patient is given 1.55 mg of I-131, a beta emitter with a half-life of 8.0 days. Assuming that none of the I-131 is eliminated from the person's body in the first 4.0 hours of treatment, what is the exposure (in Ci) during those first four hours?
Textbook Question
Complete each nuclear equation and calculate the energy change (in J/mol of reactant) associated with each (Be-9 = 9.012182 amu, Bi-209 = 208.980384 amu, He-4 = 4.002603 amu, Li-6 = 6.015122 amu, Ni-64 = 63.927969 amu, Rg-272 = 272.1535 amu, Ta-179 = 178.94593 amu, and W-179 = 178.94707 amu). a. _____ + 94Be → 63Li + 42He
