Textbook Question
The half-life of 238U is 4.5⨉109 yr. A sample of rock of mass 1.6 g produces 29 dis/s. Assuming all the radioactivity is due to 238U, find the percent by mass of 238U in the rock.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
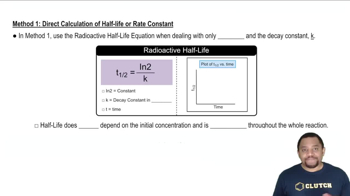
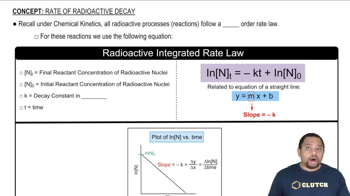
The half-life of 238U is 4.5⨉109 yr. A sample of rock of mass 1.6 g produces 29 dis/s. Assuming all the radioactivity is due to 238U, find the percent by mass of 238U in the rock.
The half-life of 232Th is 1.4⨉1010 yr. Find the number of disintegrations per hour emitted by 1.0 mol of 232Th.