Textbook Question
Balance each redox reaction occurring in basic aqueous solution. a. MnO4–(aq) + Br–(aq) → MnO2(s) + BrO3–(aq)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

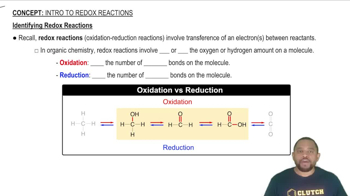
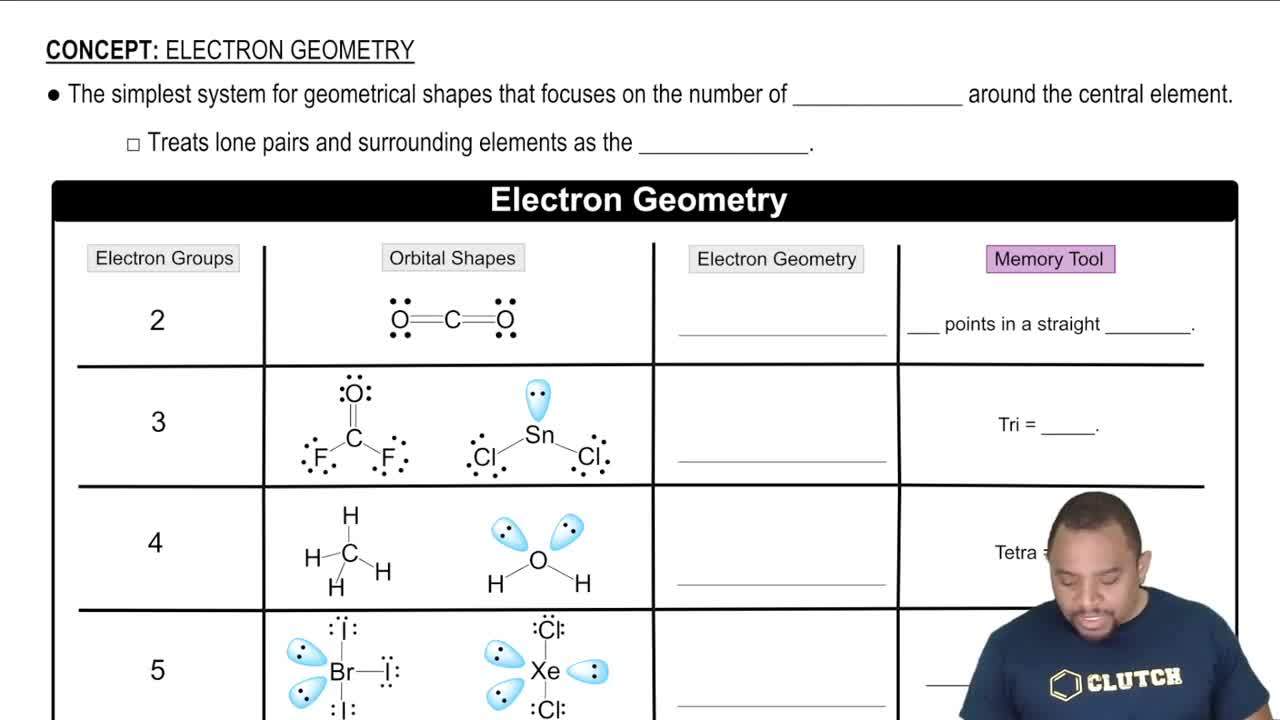
Balance each redox reaction occurring in basic aqueous solution. a. MnO4–(aq) + Br–(aq) → MnO2(s) + BrO3–(aq)
Balance each redox reaction occurring in basic aqueous solution. b. Ag(s) + CN–(aq) + O2(g) → Ag(CN)2–(aq)
Balance each redox reaction occurring in basic aqueous solution. c. NO2–(aq) + Al(s) → NH3(g) + AlO2–(aq)
Calculate the standard cell potential for each of the electro- chemical cells in Problem 43.
Consider the voltaic cell:
d. Indicate the direction of anion and cation flow in the salt bridge