Pseudogout, a condition with symptoms similar to those of gout (see Problem 126), is caused by the formation of calcium diphosphate (Ca2P2O7) crystals within tendons, cartilage, and ligaments. Calcium diphosphate will precipitate out of blood plasma when diphosphate levels become abnormally high. If the calcium concentration in blood plasma is 9.2 mg/dL, and Ksp for calcium diphosphate is 8.64⨉10-13, what minimum concentration of diphosphate results in precipitation?
Ch.18 - Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium

Chapter 18, Problem 131
The Kb of hydroxylamine, NH2OH, is 1.10 * 10^-8. A buffer solution is prepared by mixing 100.0 mL of a 0.36 M hydroxylamine solution with 50.0 mL of a 0.26 M HCl solution. Determine the pH of the resulting solution.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Calculate the moles of hydroxylamine (NH2OH) using the formula: moles = concentration (M) * volume (L).
Calculate the moles of HCl using the formula: moles = concentration (M) * volume (L).
Determine the moles of NH2OH remaining after the reaction with HCl, considering the stoichiometry of the reaction: NH2OH + HCl -> NH3OH+ + Cl-.
Calculate the concentration of NH2OH and NH3OH+ in the final solution by dividing the moles of each by the total volume of the solution in liters.
Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to find the pH: pH = pKa + log([base]/[acid]), where pKa = -log(Ka) and Ka = Kw/Kb.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Buffer Solutions
A buffer solution is a system that resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. It typically consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. In this case, hydroxylamine acts as a weak base, while HCl provides the conjugate acid, allowing the solution to maintain a relatively stable pH.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Buffer Solutions
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is a mathematical formula used to calculate the pH of a buffer solution. It is expressed as pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]), where pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka). For this problem, we need to determine the pKa of hydroxylamine from its Kb to find the pH of the buffer solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
Dissociation Constants (Ka and Kb)
Dissociation constants are equilibrium constants that describe the extent to which an acid or base dissociates in solution. Kb is the base dissociation constant, while Ka is the acid dissociation constant. The relationship between Ka and Kb for a conjugate acid-base pair is given by the equation Kw = Ka × Kb, where Kw is the ion product of water. This relationship is essential for converting Kb to Ka when calculating pH.
Recommended video:
Guided course
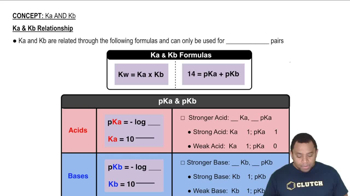
Ka and Kb Relationship
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Calculate the solubility of silver chloride in a solution that is 0.100 M in NH3.
Textbook Question
Calculate the solubility of CuX in a solution that is 0.150 M in NaCN. Ksp for CuX is 1.27⨉10-36.
Textbook Question
A 0.867-g sample of an unknown acid requires 32.2 mL of a 0.182 M barium hydroxide solution for neutralization. Assuming the acid is diprotic, calculate the molar mass of the acid.
Textbook Question
A 25.0-mL volume of a sodium hydroxide solution requires 19.6 mL of a 0.189 M hydrochloric acid for neutralization. A 10.0-mL volume of a phosphoric acid solution requires 34.9 mL of the sodium hydroxide solution for complete neutralization. Calculate the concentration of the phosphoric acid solution.
