Textbook Question
Based on molecular structure, arrange the oxyacids in order of increasing acid strength. Explain your choice. HClO3, HIO3, HBrO3

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
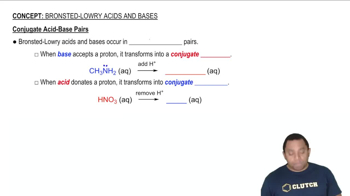
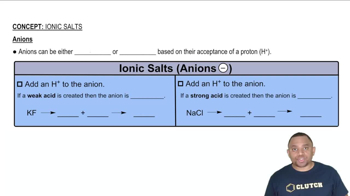
Based on molecular structure, arrange the oxyacids in order of increasing acid strength. Explain your choice. HClO3, HIO3, HBrO3
Which is a stronger base, S2– or Se2–? Explain.
Classify each species as either a Lewis acid or a Lewis base. a. Fe3+ b. BH3 c. NH3 d. F-
Classify each species as either a Lewis acid or a Lewis base. a. BeCl2
Classify each species as either a Lewis acid or a Lewis base. b. OH–