Textbook Question
Determine whether each anion is basic or neutral. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. c. NO3–

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
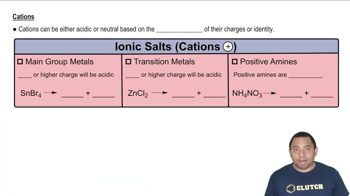
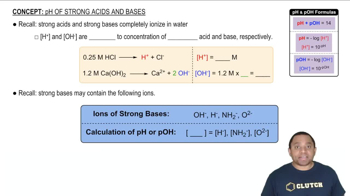
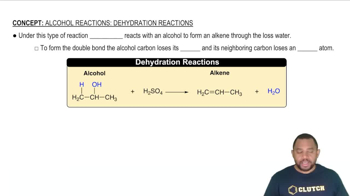
Determine whether each anion is basic or neutral. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. c. NO3–
Determine the [OH–] and pH of a solution that is 0.140 M in F–.
Determine whether each cation is acidic or pH-neutral. For those cations that are acidic, write an equation that shows how the cation acts as an acid. b. Na+
Determine whether each cation is acidic or pH-neutral. For those cations that are acidic, write an equation that shows how the cation acts as an acid. c. Co3+
Determine whether each cation is acidic or pH-neutral. For those cations that are acidic, write an equation that shows how the cation acts as an acid. d. CH2NH3+