Caffeine (C8H10N4O2) is a weak base with a pKb of 10.4. Calculate the pH of a solution containing a caffeine concentration of 455 mg/L.
Ch.17 - Acids and Bases

Chapter 17, Problem 94
A 0.135 M solution of a weak base has a pH of 11.23. Determine Kb for the base.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the relationship between pH and pOH: \( \text{pH} + \text{pOH} = 14 \). Use this to find pOH from the given pH.
Calculate the hydroxide ion concentration \([\text{OH}^-]\) using the formula \([\text{OH}^-] = 10^{-\text{pOH}}\).
Set up the expression for the base dissociation constant \(K_b\) using the formula \(K_b = \frac{[\text{OH}^-]^2}{[\text{Base}] - [\text{OH}^-]}\).
Assume that \([\text{Base}] - [\text{OH}^-] \approx [\text{Base}]\) if \([\text{OH}^-]\) is much smaller than the initial concentration of the base.
Substitute the values into the \(K_b\) expression and solve for \(K_b\).
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Weak Base and pH
A weak base is a substance that partially ionizes in solution, establishing an equilibrium between the base and its ions. The pH of a solution indicates its acidity or basicity, with values above 7 being basic. In this case, a pH of 11.23 suggests that the solution is basic, and the concentration of hydroxide ions can be derived from the pH to help calculate the base's dissociation constant.
Recommended video:
Guided course
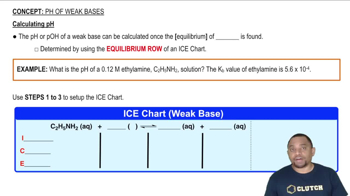
Calculating pH of Weak Bases Example
Equilibrium Constant (Kb)
The base dissociation constant (Kb) quantifies the strength of a weak base in solution. It is defined as the ratio of the concentration of the products (the ions formed) to the concentration of the reactants (the un-ionized base) at equilibrium. For a weak base, Kb can be calculated using the concentrations of the base and its ions at equilibrium, which can be derived from the pH and initial concentration.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Equilibrium Constant K
Relationship Between pH and pOH
The pH and pOH of a solution are related through the equation pH + pOH = 14 at 25°C. This relationship allows us to convert pH values into pOH values, which can then be used to find the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in the solution. Knowing the concentration of OH- is essential for calculating Kb, as it directly relates to the degree of ionization of the weak base.
Recommended video:
Guided course
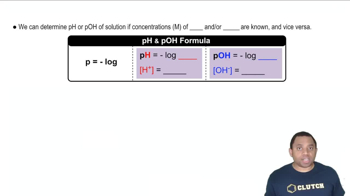
pH and pOH Calculations
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
Amphetamine (C9H13N) is a weak base with a pKb of 4.2. Calculate the pH of a solution containing an amphetamine concentration of 225 mg/L.
Textbook Question
Morphine is a weak base. A 0.150 M solution of morphine has a pH of 10.7. What is Kb for morphine?
1
views
Textbook Question
Determine if each anion acts as a weak base in solution. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. a. Br– b. ClO– c. CN– d. Cl–
1
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether each anion is basic or neutral. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. c. NO3–
Textbook Question
Determine the [OH–] and pH of a solution that is 0.140 M in F–.
