Consider the tabulated data showing the initial rate of a reaction (A → products) at several different concentrations of A. What is the order of the reaction? Write a rate law for the reaction including the value of the rate constant, k.
Ch.15 - Chemical Kinetics

Chapter 15, Problem 48a
Indicate the order of reaction consistent with each observation.
a. The half-life of the reaction gets shorter as the initial concentration is increased.
b. A plot of the natural log of the concentration of the reactant versus time yields a straight line.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the relationship between half-life and concentration for different orders of reaction.
Recall that for a zero-order reaction, the half-life decreases as the initial concentration increases.
For a first-order reaction, the half-life is independent of the initial concentration.
For a second-order reaction, the half-life increases as the initial concentration decreases.
Conclude that the observation of the half-life getting shorter as the initial concentration increases is consistent with a zero-order reaction.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Order of Reaction
The order of a reaction refers to the power to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate law. It provides insight into how the rate of reaction is affected by the concentration of reactants. Common orders include zero, first, and second, each indicating different relationships between concentration and reaction rate.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Average Bond Order
Half-Life of a Reaction
The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the concentration of a reactant to decrease to half of its initial value. For different orders of reactions, the half-life behaves differently; for example, in first-order reactions, the half-life is constant, while in second-order reactions, it increases with decreasing concentration.
Recommended video:
Guided course
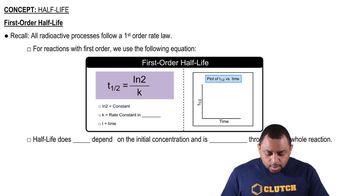
First-Order Half-Life
Kinetics and Concentration
In chemical kinetics, the relationship between reaction rate and concentration is crucial. If the half-life of a reaction decreases as the initial concentration increases, it suggests a reaction order greater than one, typically indicating a second-order reaction. This behavior highlights how changes in concentration can significantly influence reaction dynamics.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Chemical Kinetics
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The tabulated data were collected for this reaction: CH3Cl(g) + 3 Cl2(g) → CCl4( g) + 3 HCl(g)
Write an expression for the reaction rate law and calculate the value of the rate constant, k. What is the overall order of the reaction?
Textbook Question
Indicate the order of reaction consistent with each observation c. The half-life of the reaction gets longer as the initial concentration is increased.
Textbook Question
The tabulated data show the concentration of AB versus time for this reaction: AB( g)¡A( g) + B( g) Time (s) [AB] (M) 0 0.950 50 0.459 100 0.302 150 0.225 200 0.180 250 0.149 300 0.128 350 0.112 400 0.0994 450 0.0894 500 0.0812 Determine the order of the reaction and the value of the rate constant. Predict the concentration of AB at 25 s.
1
views
