Describe how to prepare each solution from the dry solute and the solvent. b. 125 g of 0.100 m NaNO3

For a solution prepared by dissolving 28.4 g of glucose (C6H12O6) in 355 g of water with a final volume of 378 mL, calculate the concentration in each unit: a. molarity, b. molality, c. percent by mass, d. mole fraction, e. mole percent.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Molarity

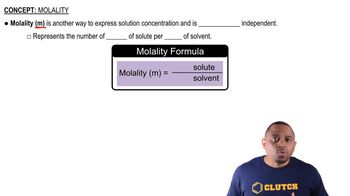
Molality
Percent by Mass

Describe how to prepare each solution from the dry solute and the solvent. c. 125 g of 1.0% NaNO3 solution by mass
A solution is prepared by dissolving 20.2 mL of methanol (CH3OH) in 100.0 mL of water at 25 °C. The final volume of the solution is 118 mL. The densities of methanol and water at this temperature are 0.782 g/mL and 1.00 g/mL, respectively. For this solution, calculate the concentration in each unit. a. molarity
A solution is prepared by dissolving 20.2 mL of methanol (CH3OH) in 100.0 mL of water at 25 °C. The final volume of the solution is 118 mL. The densities of methanol and water at this temperature are 0.782 g/mL and 1.00 g/mL, respectively. For this solution, calculate the concentration in each unit. b. molality
A solution is prepared by dissolving 20.2 mL of methanol (CH3OH) in 100.0 mL of water at 25 °C. The final volume of the solution is 118 mL. The densities of methanol and water at this temperature are 0.782 g/mL and 1.00 g/mL, respectively. For this solution, calculate the concentration in each unit. c. percent by mass
