Nitrogen has a normal boiling point of 77.3 K and a melting point (at 1 atm) of 63.1 K. Its critical temperature is 126.2 K and its critical pressure is 2.55×104 torr. It has a triple point at 63.1 K and 94.0 torr. Sketch the phase diagram for nitrogen. Does nitrogen have a stable liquid state at 1 atm?
Ch.12 - Liquids, Solids & Intermolecular Forces

Chapter 12, Problem 77a
The phase diagram for sulfur is shown here. The rhombic and monoclinic states are two solid states with different structures. a. Below what pressure does solid sulfur sublime?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the phase transition line between the solid and gas phases on the phase diagram for sulfur. This line represents the conditions under which solid sulfur can sublime directly into gas.
Locate the point on the phase diagram where the solid-gas transition line starts. This point indicates the minimum pressure at which solid sulfur begins to sublime.
Follow the solid-gas transition line vertically downwards to find the lowest pressure at which sublimation occurs.
Note the pressure value at this lowest point. This is the pressure below which solid sulfur can sublime.
Understand that at pressures lower than this value, solid sulfur will not remain stable and will transition directly to the gaseous state without passing through a liquid phase.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Phase Diagram
A phase diagram is a graphical representation that shows the phases of a substance at various temperatures and pressures. It delineates the boundaries between different states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—and indicates conditions under which these phases coexist. Understanding phase diagrams is crucial for predicting the behavior of substances under varying environmental conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
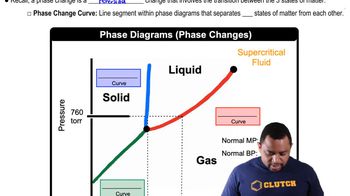
Phase Changes in Diagrams
Sublimation
Sublimation is the process by which a solid transitions directly into a gas without passing through the liquid phase. This phenomenon occurs under specific temperature and pressure conditions, typically at low pressures for certain substances. In the context of sulfur, identifying the pressure below which sublimation occurs is essential for understanding its phase behavior.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sublimation Phase Change Example
Solid States of Sulfur
Sulfur can exist in different solid forms, primarily rhombic and monoclinic, each with distinct crystal structures and properties. The rhombic form is stable at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, while the monoclinic form is stable at higher temperatures. Recognizing these solid states is important for interpreting the phase diagram and understanding the conditions under which sublimation occurs.
Recommended video:
Guided course
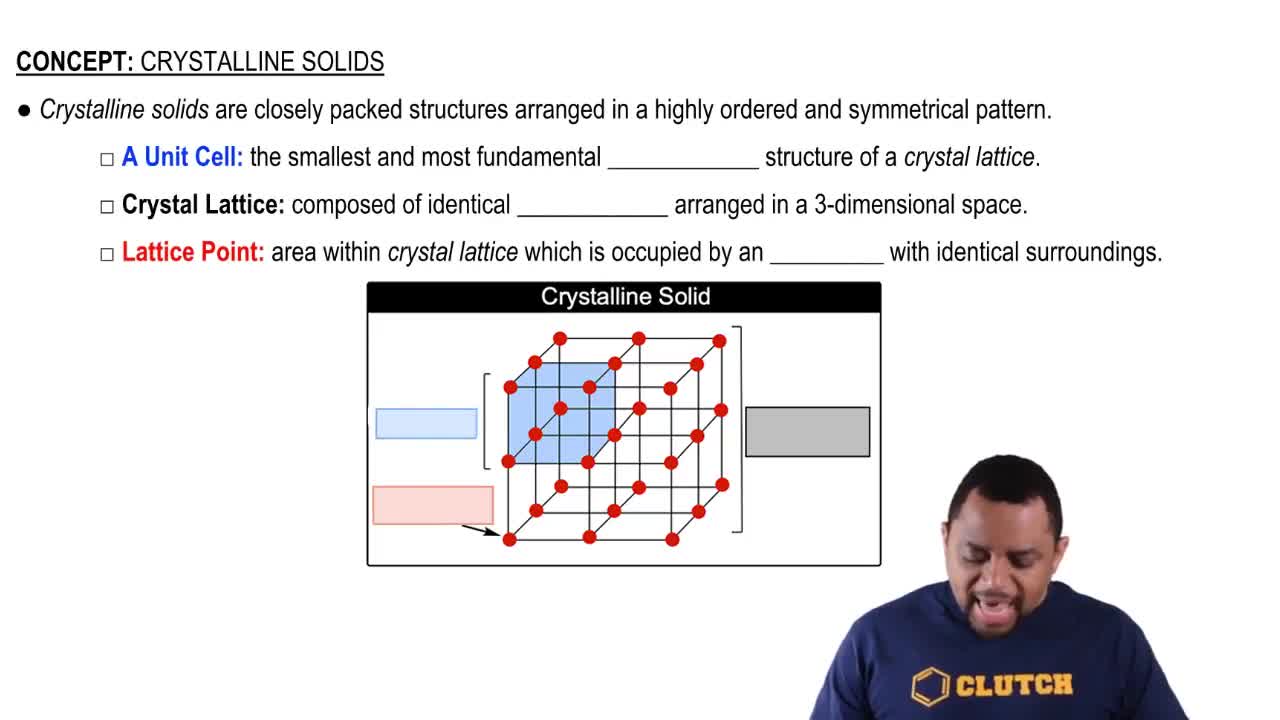
Crystalline Solids Structure
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Argon has a normal boiling point of 87.2 K and a melting point (at 1 atm) of 84.1 K. Its critical temperature is 150.8 K and its critical pressure is 48.3 atm. It has a triple point at 83.7 K and 0.68 atm. Sketch the phase diagram for argon. Which has the greater density, solid argon or liquid argon?
Textbook Question
The phase diagram for sulfur is shown here. The rhombic and monoclinic states are two solid states with different structures. b. Which of the two solid states of sulfur is more dense?
Textbook Question
Water is a good solvent for many substances. What is the molecular basis for this property, and why is it significant?
