Textbook Question
According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the highest bond energy? O2, O2- , O22-

 Tro 5th Edition
Tro 5th Edition Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory
Ch.11 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, VSEPR & MO Theory Problem 82
Problem 82 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
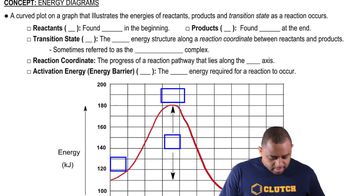

According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the highest bond energy? O2, O2- , O22-
According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the shortest bond length? O2, O2- , O22-
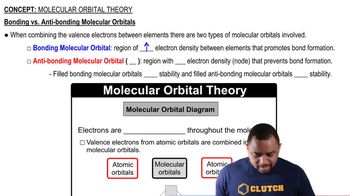
Draw an MO energy diagram for CO. (Use the energy ordering of O2.) Predict the bond order and make a sketch of the lowest energy bonding molecular orbital.
The genetic code is based on four different bases with the structures shown here. Assign a geometry and hybridization to each interior atom in these four bases. d. guanine