The cyanate ion (OCN-) and the fulminate ion (CNO-) share the same three atoms but have vastly different properties. The cyanate ion is stable, while the fulminate ion is unstable and forms explosive compounds. The resonance structures of the cyanate ion are explored in Example 9.8. Draw Lewis structures for the fulminate ion—including possible resonance forms— and use formal charge to explain why the fulminate ion is less stable (and therefore more reactive) than the cyanate ion.
Ch.9 - Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model

Chapter 9, Problem 98a,d
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. a. C3H8 d. CH3COOH
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the number of valence electrons for each atom in the compound. Carbon has 4, hydrogen has 1, and oxygen has 6 valence electrons.
For C_3H_8 (propane), arrange the three carbon atoms in a chain. Each carbon atom forms four bonds. Connect the carbon atoms with single bonds and attach hydrogen atoms to satisfy the valence of each carbon.
For CH_3COOH (acetic acid), start by identifying the functional groups. The CH_3 group is a methyl group, and COOH is a carboxylic acid group.
In CH_3COOH, connect the CH_3 group to the carbon of the COOH group. The carbon in the COOH group is double-bonded to one oxygen and single-bonded to the OH group.
Ensure that all atoms have a complete octet (except hydrogen, which should have 2 electrons) and adjust any lone pairs on oxygen atoms as needed.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist. They use dots to represent electrons and lines to represent bonds between atoms. Understanding how to draw Lewis structures is essential for visualizing molecular geometry and predicting the behavior of molecules in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lewis Dot Structures: Ions
Condensed Structural Formulas
Condensed structural formulas provide a shorthand way of representing the structure of a molecule, showing how atoms are connected without depicting all the bonds explicitly. For example, in CH3COOH, the formula indicates that there are three hydrogen atoms bonded to a carbon, which is also bonded to another carbon that has a hydroxyl group (-OH). This format is crucial for translating into Lewis structures.
Recommended video:
Guided course
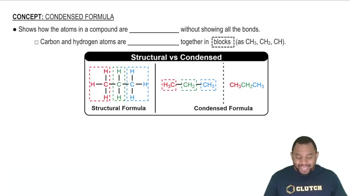
Condensed Formula
Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom and are involved in forming bonds with other atoms. The number of valence electrons determines how atoms will bond and the overall structure of the molecule. Knowing how to count and distribute valence electrons is vital for accurately drawing Lewis structures and understanding molecular stability.
Recommended video:
Guided course
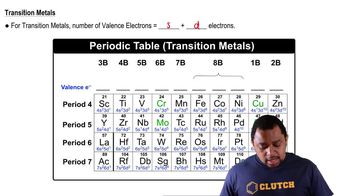
Transition Metals Valence Electrons
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. b. CH3OCH3
Textbook Question
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. c. CH3COCH3
Textbook Question
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. e. CH3CHO
