Each compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds. Write ionic Lewis structures for each, including the covalent structure for the ion in brackets. Write resonance structures if necessary. a. BaCO3

Carbon ring structures are common in organic chemistry. Draw a Lewis structure for each carbon ring structure, including any necessary resonance structures. a. C4H8 b. C4H4 c. C6H12 d. C6H6
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Lewis Structures

Resonance Structures

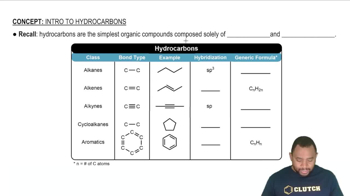
Hydrocarbons
Each compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds. Write ionic Lewis structures for each, including the covalent structure for the ion in brackets. Write resonance structures if necessary. b. Ca(OH)2 c. KNO3 d. LiIO
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. The simplest amino acid is glycine (H2NCH2COOH). Draw a Lewis structure for glycine. (Hint: The central atoms in the skeletal structure are nitrogen and the two carbon atoms. Each oxygen atom is bonded directly to the right-most carbon atom.)
Formic acid is responsible for the sting of ant bites. By mass, formic acid is 26.10% C, 4.38% H, and 69.52% O. The molar mass of formic acid is 46.02 g/mol. Determine the molecular formula of formic acid and draw its Lewis structure.
Diazomethane is a highly poisonous, explosive compound because it readily evolves N2. Diazomethane has the following composition by mass: 28.57% C; 4.80% H; and 66.64% N. The molar mass of diazomethane is 42.04 g/mol. Find the molecular formula of diazomethane, draw its Lewis structure, and assign formal charges to each atom. Why is diazomethane not very stable? Explain.
