Textbook Question
Use the periodic table to determine each quantity.
b. the number of 3d electrons in Cr

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
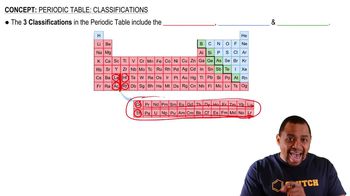
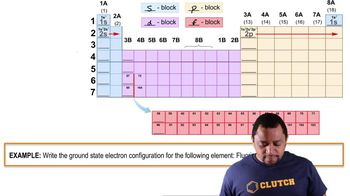
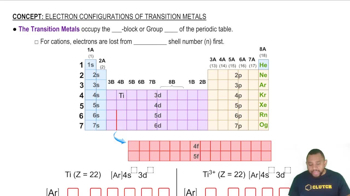
Use the periodic table to determine each quantity.
b. the number of 3d electrons in Cr
Name an element in the fourth period (row) of the periodic table with the following: a. five valence electrons
Name an element in the fourth period (row) of the periodic table with the following: b. four 4p electrons
Name an element in the fourth period (row) of the periodic table with the following: d. full s and p sublevels
Name an element in the third period (row) of the periodic table with the following: a. three valence electrons
Name an element in the third period (row) of the periodic table with the following: b. four 3p electrons