A 2.85-g lead weight, initially at 10.3 °C, is submerged in 7.55 g of water at 52.3 °C in an insulated container. What is the final temperature of both substances at thermal equilibrium?

Should you carry out a chemical reaction under conditions of constant volume or constant pressure to obtain the largest possible amount of heat, if there is a large increase in the number of moles of gas? Explain.
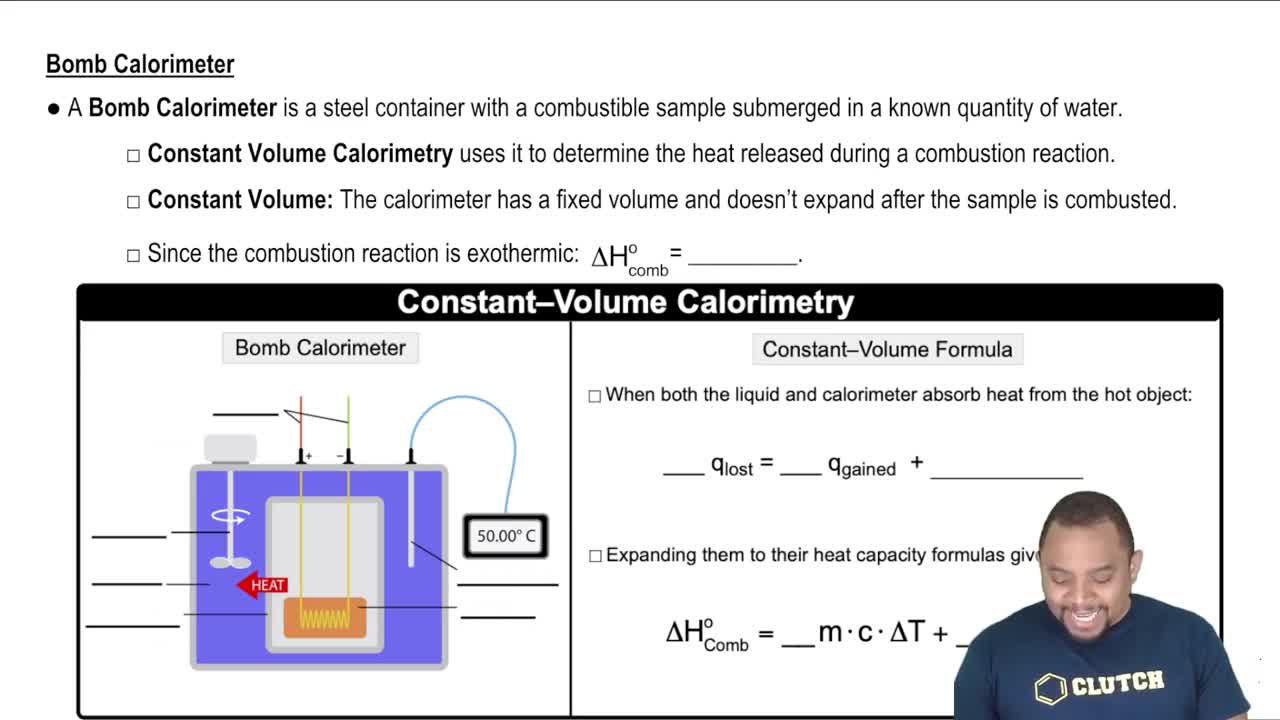
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Enthalpy and Heat Transfer

Ideal Gas Law and Molar Volume

Constant Volume vs. Constant Pressure Conditions
Two substances, A and B, initially at different temperatures, come into contact and reach thermal equilibrium. The mass of substance A is 6.15 g and its initial temperature is 20.5 °C. The mass of substance B is 25.2 g and its initial temperature is 52.7 °C. The final temperature of both substances at thermal equilibrium is 46.7 °C. If the specific heat capacity of substance B is 1.17 J/g•°C, what is the specific heat capacity of substance A?
Exactly 1.5 g of a fuel burns under conditions of constant pressure and then again under conditions of constant volume. In measurement A the reaction produces 25.9 kJ of heat, and in measurement B the reaction produces 23.3 kJ of heat. Which measurement (A or B) corresponds to conditions of constant pressure? Explain.
When 0.514 g of biphenyl (C12H10) undergoes combustion in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature rises from 25.8 °C to 29.4 °C. Find ΔErxn for the combustion of biphenyl in kJ/mol biphenyl. The heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter, determined in a separate experiment, is 5.86 kJ/°C.
Mothballs are composed primarily of the hydrocarbon naphthalene (C10H8). When 1.025 g of naphthalene burns in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature rises from 24.25 °C to 32.33 °C. Find ΔErxn for the combustion of naphthalene. The heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter, determined in a separate experiment, is 5.11 kJ/°C.
Zinc metal reacts with hydrochloric acid according to the balanced equation: Zn(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) When 0.103 g of Zn(s) is combined with enough HCl to make 50.0 mL of solution in a coffee-cup calorimeter, all of the zinc reacts, raising the temperature of the solution from 22.5 °C to 23.7 °C. Find ΔHrxn for this reaction as written. (Use 1.0 g/mL for the density of the solution and 4.18 J/g•°C as the specific heat capacity.)
