Textbook Question
Refer to the nomenclature flowchart (Figure 3.11) to name each compound. a. HNO2(aq)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

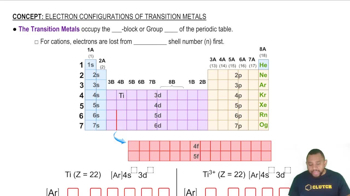
Refer to the nomenclature flowchart (Figure 3.11) to name each compound. a. HNO2(aq)
Refer to the nomenclature flowchart (Figure 3.11) to name each compound. a. KClO3 b. I2O5 c. PbSO4
Refer to the nomenclature flowchart (Figure 3.11) to name each compound. a. XeO3 b. KClO
Calculate the formula mass for each compound. a. NO2 c. C6H12O6 b. C4H10 d. Cr(NO3)3
Calculate the formula mass for each compound. a. MgBr2 b. HNO2 c. CBr4 d. Ca(NO3)2