Textbook Question
List all the possible products for each alkane substitution reaction. (Assume monosubstitution.) b. CH3CH2CH3 + Cl2 → d.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
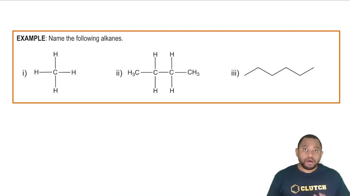
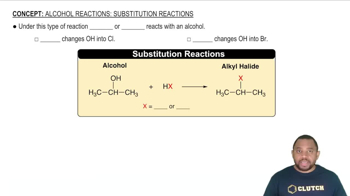

List all the possible products for each alkane substitution reaction. (Assume monosubstitution.) b. CH3CH2CH3 + Cl2 → d.
List all the possible products for each alkane substitution reac- tion. (Assume monosubstitution.)
c. CH2Cl2 + Br2 →
List all the possible products for each alkane substitution reaction. (Assume monosubstitution.) a.CH4 +Cl2 → b. CH3CH2Br + Br2 → d. CH3CHBr2 + Br2 →
Write structural formulas for each of the possible isomers of n-pentyne that are formed by moving the position of the triple bond.
Name each alkene. c.