Textbook Question
Draw the structure of each carboxylic acid or ester. a. pentanoic acid

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
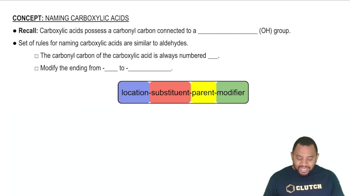
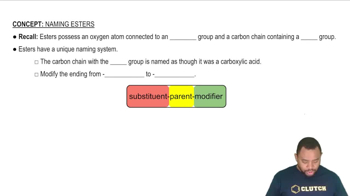

Draw the structure of each carboxylic acid or ester. a. pentanoic acid
Draw the structure of each carboxylic acid or ester. b. methyl hexanoate
Draw the structure of each carboxylic acid or ester. c. 3-ethylheptanoic acid
Determine the products of each carboxylic acid reaction. a.
Determine the products of each carboxylic acid reaction. b.
Determine the products of each carboxylic acid reaction. a.