Textbook Question
Draw the correct structure for each compound. c. 3,3-dimethyl-1-pentyne

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
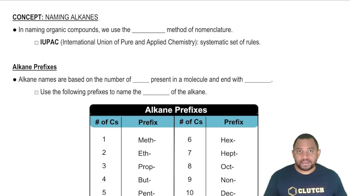
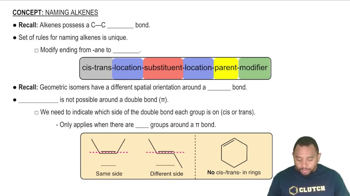
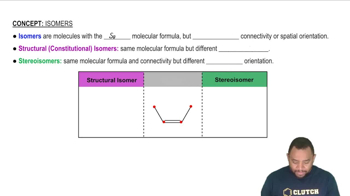
Draw the correct structure for each compound. c. 3,3-dimethyl-1-pentyne
Draw the correct structure for each compound. d. 5-ethyl-3,6-dimethyl-2-heptene
Draw the correct structure for each compound.
b. 1-heptyne
List the products of each alkene addition reaction. c.
List the products of each alkene addition reaction. d.