Textbook Question
Determine the number of protons and the number of electrons in each ion. b. Se2-

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
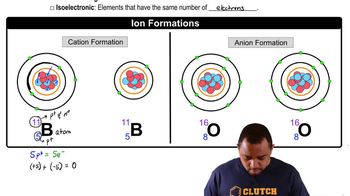
Determine the number of protons and the number of electrons in each ion. b. Se2-
Determine the number of protons and the number of electrons in each ion. c. Ga3+
Determine the number of protons and the number of electrons in each ion. d. Sr2+
Predict the charge of the ion formed by each element. a. Mg b. N d. Na
Predict the charge of the ion formed by each element. c. F
Fill in the blanks to complete the table. Symbol Ion Formed Number of Electrons in Ion Number of Protons in Ion Ca Ca2+ ______ ______ ______ Be2+ 2 ______ Se ______ ______ 34 In ______ ______ 49