Textbook Question
Classify each element as an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, halogen, or noble gas. a. F b. Sr c. K d. Ne e. At
2
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
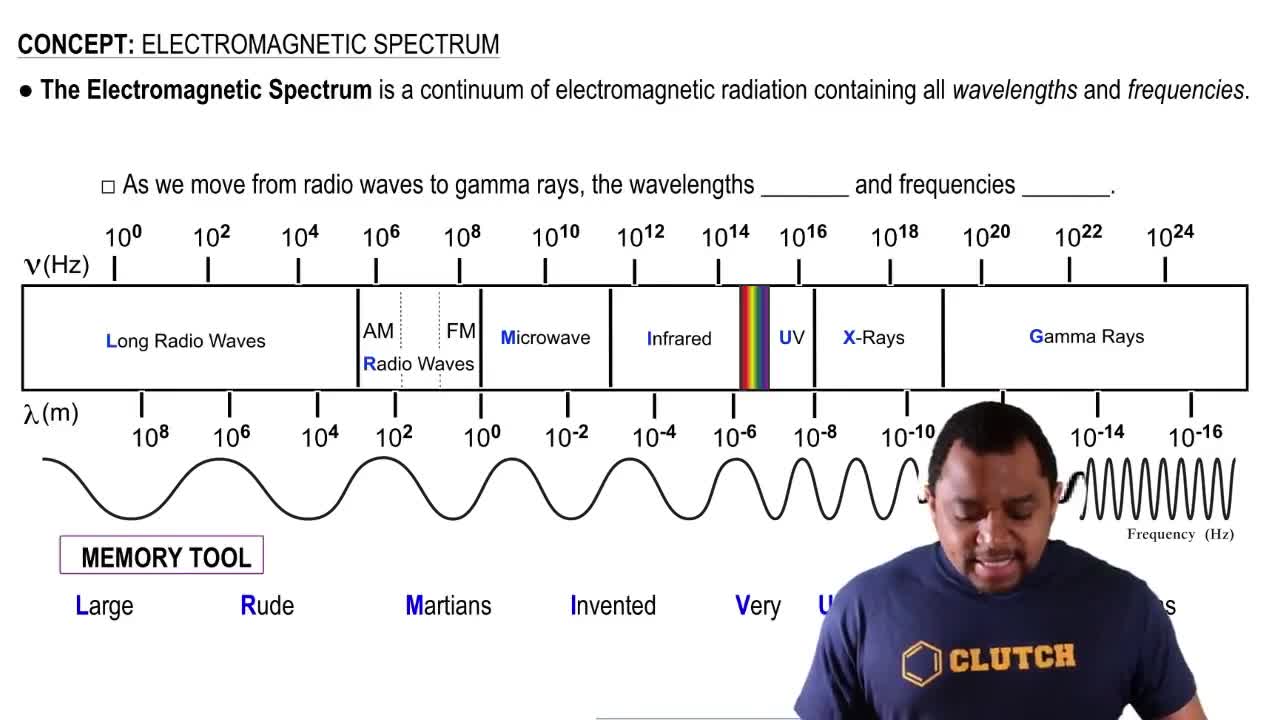

Classify each element as an alkali metal, alkaline earth metal, halogen, or noble gas. a. F b. Sr c. K d. Ne e. At
Which pair of elements do you expect to be most similar? Why? a. N and Ni b. Mo and Sn c. Na and Mg d. Cl and F e. Si and P
Which pair of elements do you expect to be most similar? Why? a. nitrogen and oxygen b. titanium and gallium c. lithium and sodium d. germanium and arsenic e. argon and bromine
The atomic mass of fluorine is 18.998 amu, and its mass spectrum shows a large peak at this mass. The atomic mass of chlorine is 35.45 amu, yet the mass spectrum of chlorine does not show a peak at this mass. Explain the difference.