Identify the elements that have molecules as their basic units. a. hydrogen b. iodine c. lead d. oxygen
Ch.2 - Atoms & Elements

Chapter 2, Problem 30
An automobile gasoline tank holds 21 kg of gasoline. When the gasoline burns, 84 kg of oxygen is consumed, and carbon dioxide and water are produced. What is the total combined mass of carbon dioxide and water that is produced?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
1. According to the law of conservation of mass, the total mass of the reactants (the substances that start a chemical reaction) must equal the total mass of the products (the substances that are produced by a chemical reaction). This means that the mass of the gasoline and the oxygen that are consumed must equal the mass of the carbon dioxide and water that are produced.
2. To find the total combined mass of carbon dioxide and water that is produced, you need to add the mass of the gasoline that is burned to the mass of the oxygen that is consumed. This is because the gasoline and the oxygen are the reactants in this chemical reaction, and their total mass must equal the total mass of the products.
3. The problem states that the gasoline tank holds 21 kg of gasoline and that 84 kg of oxygen is consumed when the gasoline burns. Therefore, you need to add these two masses together to find the total mass of the reactants.
4. The sum of the mass of the gasoline and the mass of the oxygen gives you the total combined mass of carbon dioxide and water that is produced. This is because the law of conservation of mass states that the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products in a chemical reaction.
5. Therefore, the total combined mass of carbon dioxide and water that is produced when the gasoline burns and the oxygen is consumed is the sum of the mass of the gasoline and the mass of the oxygen.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Law of Conservation of Mass
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This principle implies that the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products. In the context of the combustion of gasoline, the mass of gasoline and oxygen consumed will equal the mass of carbon dioxide and water produced.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Law of Conservation of Mass
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions based on balanced chemical equations. It allows us to determine the proportions of substances involved in a reaction. In this case, knowing the amounts of gasoline and oxygen helps us calculate the resulting masses of carbon dioxide and water produced during combustion.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Stoichiometry Concept
Combustion Reaction
A combustion reaction is a chemical process in which a substance (typically a hydrocarbon like gasoline) reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy. The general form of a combustion reaction can be represented as: hydrocarbon + O2 → CO2 + H2O. Understanding this type of reaction is essential for predicting the products and their masses in the given scenario.
Recommended video:
Guided course
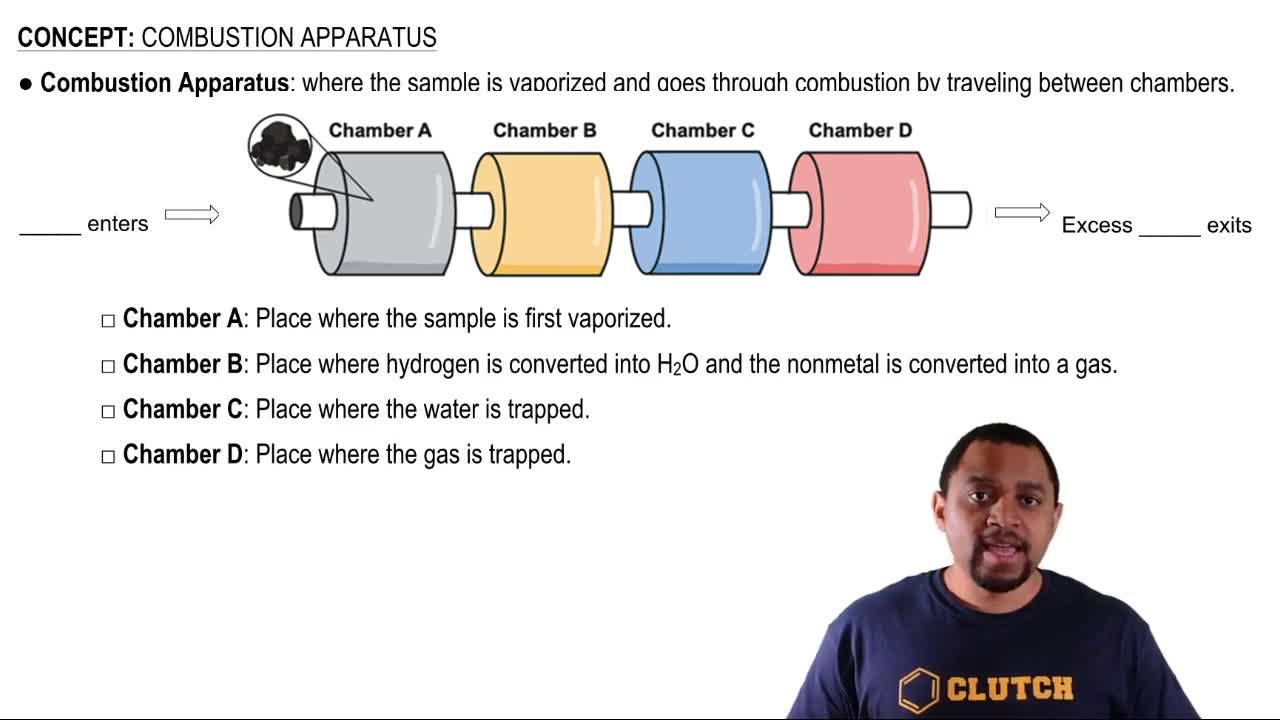
Combustion Apparatus
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
A hydrogen-filled balloon is ignited and 1.50 g of hydrogen is reacted with 12.0 g of oxygen. How many grams of water vapor form? (Assume that water vapor is the only product.)
2
views
Textbook Question
Two samples of carbon tetrachloride are decomposed into their constituent elements. One sample produces 38.9 g of carbon and 448 g of chlorine, and the other sample produces 14.8 g of carbon and 134 g of chlorine. Are these results consistent with the law of definite proportions? Explain your answer.
1
rank
Textbook Question
The mass ratio of sodium to fluorine in sodium fluoride is 1.21:1. A sample of sodium fluoride produces 28.8 g of sodium upon decomposition. How much fluorine (in grams) forms?
