Calculate E°cell for each balanced redox reaction and determine if the reaction is spontaneous as written. a. O2(g) + 2 H2O(l) + 4 Ag(s) → 4 OH–(aq) + 4 Ag+(aq) b. Br2(l) + 2 I–(aq) → 2 Br–(aq) + I2(s)
Ch.19 - Electrochemistry
Chapter 19, Problem 64
Which of the following metals is the best reducing agent? a. Mn b. Al c. Ni d. Cr
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
insert step 1> Identify the concept of a reducing agent. A reducing agent is a substance that loses electrons and is oxidized in a chemical reaction.
insert step 2> Consider the standard reduction potentials for each metal. The more negative the reduction potential, the better the metal is at losing electrons, making it a better reducing agent.
insert step 3> Look up the standard reduction potentials for each metal: Mn, Al, Ni, and Cr.
insert step 4> Compare the reduction potentials. The metal with the most negative reduction potential is the best reducing agent.
insert step 5> Determine which metal has the most negative reduction potential and conclude that it is the best reducing agent among the options provided.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Reducing Agents
A reducing agent is a substance that donates electrons in a chemical reaction, thereby reducing another substance. The strength of a reducing agent is determined by its ability to lose electrons easily. Metals tend to be good reducing agents because they have low ionization energies and can readily give up their valence electrons.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
Electrochemical Series
The electrochemical series is a list of elements organized by their standard electrode potentials. Metals that are higher in the series are more likely to be oxidized and act as reducing agents. Understanding where a metal falls in this series helps predict its reactivity and ability to reduce other substances.
Recommended video:
Guided course
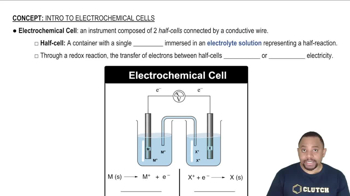
Electrochemical Cells
Metal Reactivity
Metal reactivity refers to how readily a metal can participate in chemical reactions, particularly oxidation-reduction reactions. Generally, alkali and alkaline earth metals are more reactive than transition metals. In the context of the question, comparing the reactivity of Mn, Al, Ni, and Cr will help identify which is the best reducing agent.
Recommended video:
Guided course
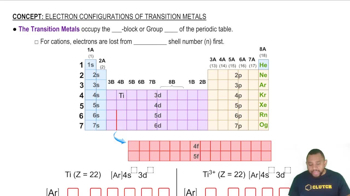
Transition Metals
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Calculate E°cell for each balanced redox reaction and determine if the reaction is spontaneous as written. c. PbO2(s) + 4 H+(aq) + Sn(s) → Pb2+(aq) + 2 H2O(l) + Sn2+(aq)
Textbook Question
Which metal cation is the best oxidizing agent? a. Pb2+ b. Cr3+ c. Fe2+ d. Sn2+
Textbook Question
Use tabulated electrode potentials to calculate ∆G°rxn for each reaction at 25 °C. b. Br2(l) + 2 Cl–(aq) → 2 Br–(aq) + Cl2(g) c. MnO2(s) + 4 H+(aq) + Cu(s) → Mn2+(aq) + 2 H2O(l) + Cu2+(aq)
Textbook Question
Use tabulated electrode potentials to calculate ∆G°rxn for each reaction at 25 °C. a. 2 Fe3+(aq) + 3 Sn(s) → 2 Fe(s) + 3 Sn2+(aq) b. O2(g) + 2 H2O(l) + 2 Cu(s) → 4 OH–(aq) + 2 Cu2+(aq) c. Br2(l) + 2 I–(aq) → 2 Br–(aq) + I2(s)
Textbook Question
Calculate the equilibrium constant for each of the reactions in Problem 65.
