Textbook Question
Calculate the molar solubility of barium fluoride in each liquid or solution. c. 0.15 M NaF

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
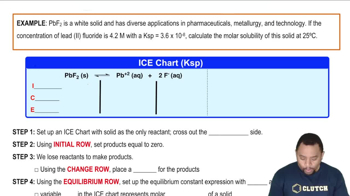

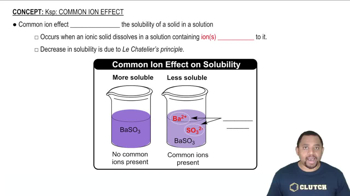
Calculate the molar solubility of barium fluoride in each liquid or solution. c. 0.15 M NaF
Calculate the molar solubility of MX (Ksp = 1.27⨉10-36) in each liquid or solution. b. 0.25 M MCl2
Calculate the molar solubility of calcium hydroxide in a solution buffered at each pH. a. pH = 4
Calculate the molar solubility of calcium hydroxide in a solution buffered at each pH. b. pH = 7
Calculate the molar solubility of calcium hydroxide in a solution buffered at each pH. c. pH = 9