Consider the titration of a 20.0-mL sample of 0.105 M HC2H3O2 with 0.125 M NaOH. Determine each quantity. b. the volume of added base required to reach the equivalence point

A 30.0-mL sample of 0.165 M propanoic acid is titrated with 0.300 M KOH. Calculate the pH at each volume of added base: 5 mL.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Acid-Base Titration
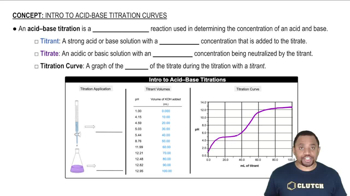
Weak Acid and Strong Base Reaction

Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation

A 30.0-mL sample of 0.165 M propanoic acid is titrated with 0.300 M KOH. Calculate the pH at each volume of added base: 0 mL, 5 mL, 10 mL, equivalence point, one-half equivalence point, 20 mL, 25 mL. Sketch the titration curve.
A 30.0-mL sample of 0.165 M propanoic acid is titrated with 0.300 M KOH. Calculate the pH at each volume of added base: 0 mL.
A 30.0-mL sample of 0.165 M propanoic acid is titrated with 0.300 M KOH. Calculate the pH at each volume of added base: 10 mL.
A 30.0-mL sample of 0.165 M propanoic acid is titrated with 0.300 M KOH. Calculate the pH at each volume of added base: equivalence point.
A 30.0-mL sample of 0.165 M propanoic acid is titrated with 0.300 M KOH. Calculate the pH at each volume of added base: one-half equivalence point.
